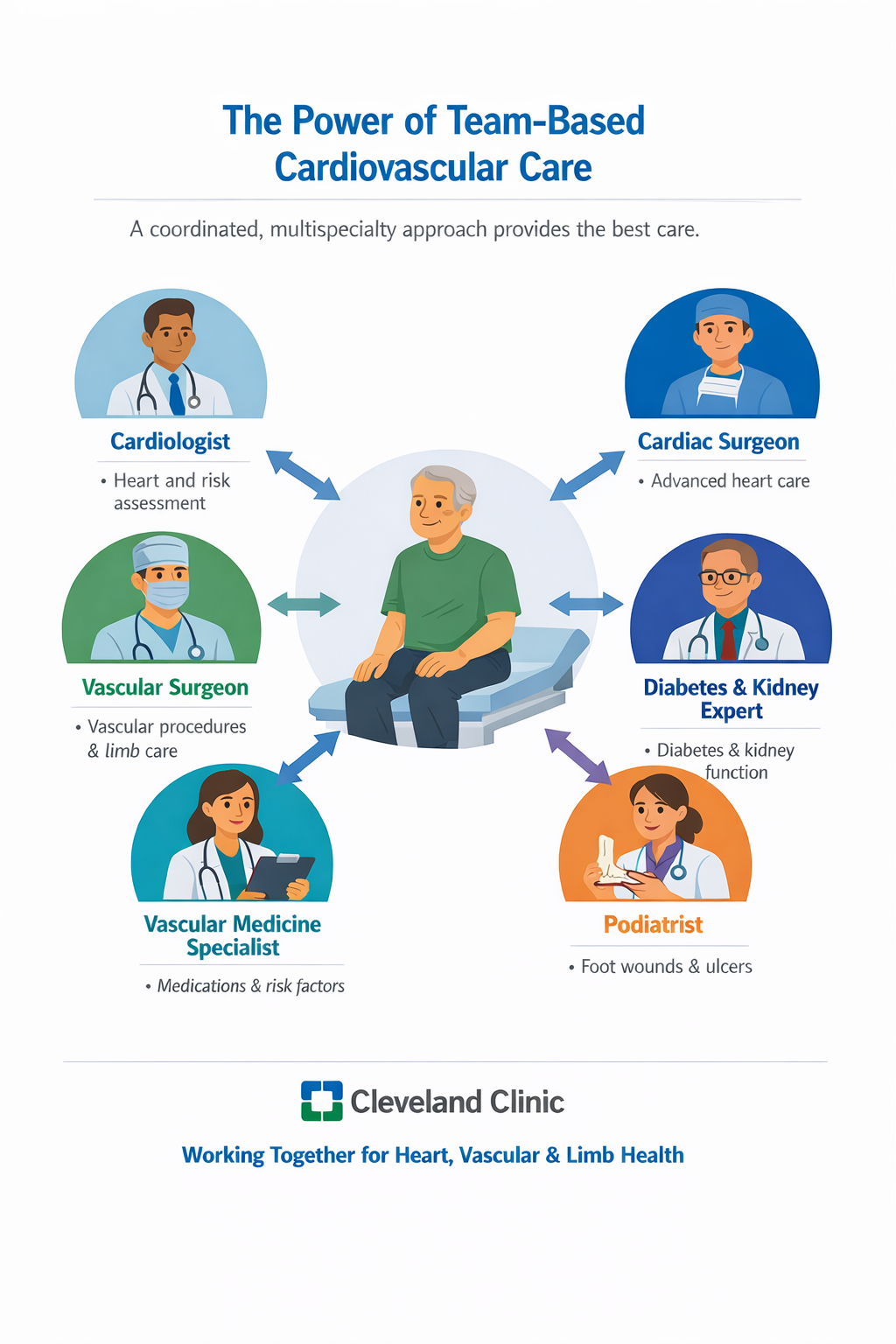
Team based cardiovascular care and vascular surgery at The Cleveland Clinic
Why Team-Based Cardiovascular Care Matters: The Power of Multispecialty Care
Cardiovascular disease is complex. It affects the heart, blood vessels, brain, kidneys, and limbs—and often all at the same time. No single doctor can manage every part of this system alone. That is why modern cardiovascular care increasingly relies on multidisciplinary teams that bring together cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, vascular surgeons, podiatrists, and vascular medicine specialists.
As a vascular surgeon working on a collaborative team, I see every day how coordinated care improves outcomes, reduces complications, and saves limbs and lives.
The Evidence: Multidisciplinary Care Reduces Amputation Risk
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a leading cause of limb loss. The ACC/AHA guidelines for PAD emphasize that multidisciplinary limb salvage teams reduce amputation rates and improve healing. These teams typically include:
Vascular surgeons to restore blood flow
Podiatrists to manage foot wounds and prevent ulcers
Wound care specialists and nurses
Endocrinologists to manage diabetes
Vascular medicine specialists to optimize medications
Primary care and rehabilitation specialists
Research shows that when these specialists work together, patients are more likely to heal wounds, avoid infection, and keep their limbs.
Team Care Is Also Critical Before Vascular Surgery
The same team-based approach is essential before major vascular procedures such as:
Carotid artery revascularization (to prevent stroke)
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair
Peripheral vascular interventions to improve leg circulation
Patients with vascular disease often also have heart disease, lung disease, diabetes, and kidney disease. These conditions increase the risk of surgery if not carefully evaluated and optimized.
This is where cardiologists and cardiac surgeons play a crucial role. They help:
Assess heart function and coronary artery disease
Optimize medications like statins and blood pressure drugs
Reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and heart failure during and after surgery
Provide rapid intervention if complications occur
Why Cleveland Clinic’s Model Matters
Cleveland Clinic is recognized worldwide as a leader in cardiovascular care. One reason for this success is its integrated, team-based model, where specialists work closely together rather than in isolation.
At Cleveland Clinic, vascular surgeons collaborate daily with:
Interventional cardiologists
Cardiac surgeons
Podiatrists and wound specialists
Vascular medicine specialists
Anesthesiologists and critical care teams
This approach allows care to be personalized, coordinated, and evidence-based, improving both short-term safety and long-term outcomes.
Whole-Patient Care: More Than Just a Procedure
Whether a patient is undergoing carotid surgery, aneurysm repair, or limb salvage treatment, the goal is not just to fix a single artery. The goal is to protect the whole patient—their brain, heart, kidneys, and mobility.
Team-based care ensures that:
Stroke risk is minimized
Heart attack risk is reduced
Blood pressure and cholesterol are optimized
Diabetes is controlled
Recovery and rehabilitation are supported
This is the essence of value-based, personalized cardiovascular care.
A Message of Hope
Complex cardiovascular disease requires complex solutions—and the best solutions come from teams working together. Multidisciplinary care has been shown to reduce amputations, improve surgical outcomes, and save lives.
If you or a loved one has PAD, carotid disease, or an aneurysm, ask whether your care team includes multiple specialists working together. Coordinated cardiovascular care is not just a convenience—it is a proven strategy to achieve the best possible outcome.
At Cleveland Clinic, this collaborative model is at the heart of everything we do.
Here is a patient-friendly checklist you can place in your blog, clinic materials, or community outreach handouts. It is written at an 8th–9th grade reading level and helps patients understand who should be on their cardiovascular care team and why each role matters.
Who Is on My Cardiovascular Care Team? — Patient Checklist
Modern cardiovascular care works best when multiple specialists work together. Use this checklist to understand who may be involved in your care and what each team member does.
✅ Core Members of My Cardiovascular Care Team
☐ Primary Care Doctor (Family Medicine or Internal Medicine)
What they do:
Coordinates your overall care
Manages blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes
Refers you to specialists when needed
☐ Cardiologist (Heart Specialist)
What they do:
Evaluates heart function and coronary artery disease
Reduces risk of heart attack and heart failure
Optimizes heart medications before and after surgery
☐ Vascular Surgeon
What they do:
Treats blocked or weakened arteries
Performs procedures for PAD, carotid disease, and aneurysms
Leads limb salvage and vascular intervention care
☐ Vascular Medicine Specialist
What they do:
Manages artery and vein conditions with medications
Helps control risk factors like cholesterol and blood pressure
Coordinates long-term vascular prevention plans
☐ Cardiac Surgeon (Heart Surgeon)
What they do:
Performs heart bypass or valve surgery when needed
Assists with complex heart conditions before vascular procedures
Helps manage high-risk surgical patients
☐ Podiatrist (Foot Specialist)
What they do:
Treats foot ulcers and wounds
Prevents diabetic foot infections
Plays a key role in limb salvage programs
✅ Additional Specialists Who May Be Part of My Team
☐ Endocrinologist (Diabetes Specialist)
Helps control blood sugar and prevent complications
☐ Nephrologist (Kidney Specialist)
Manages kidney disease, especially in PAD and heart patients
☐ Wound Care Team / Nurses
Provides advanced wound treatment and dressing care
☐ Physical Therapist / Rehabilitation Team
Helps restore walking, strength, and mobility
☐ Nutritionist or Dietitian
Guides heart-healthy and vascular-friendly diets
✅ Questions Patients Should Ask
“Who is coordinating my cardiovascular care?”
“Are all my specialists communicating with each other?”
“Do I have a vascular surgeon and cardiologist involved in my case?”
“If I have a foot ulcer, can I see a limb salvage team?”
“Who can help me reduce my risk of heart attack and stroke?”
✅ Why a Team Matters
Patients with vascular disease often also have:
Heart disease
Diabetes
Kidney disease
Lung disease
A team approach helps:
Lower amputation risk
Prevent heart attacks and strokes
Reduce surgical complications
Improve healing and recovery
Team-based care = better outcomes and longer life.
Bottom Line for Patients
You deserve more than one opinion—you deserve a coordinated team.
If you have PAD, carotid disease, or an aneurysm, ask if your care includes multiple specialists working together.
The best cardiovascular care is collaborative, personalized, and proactive.